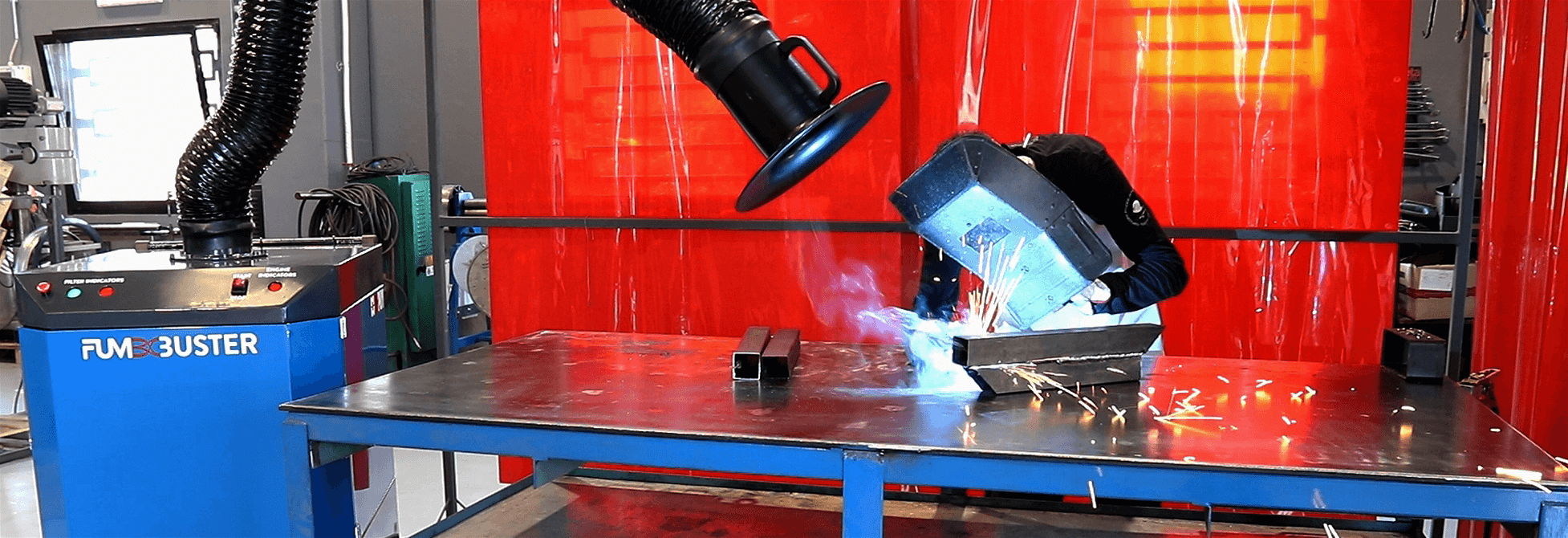
It has now been ascertained that the chemical risk of welding derives from the development of the fumes released during the heating and melting phase of the material to be welded.
The harmful substances are generated by the processed material itself, which remains in suspension in the air in the form of metal microparticles or metal derivatives.
These microparticles are rich in nickel and hexavalent chromium, with a size of 0.01 – 0.1 µm. Once inhaled, these microparticles can penetrate inside the lungs and, with time, in the blood.
The harmful substances are generated by the processed material itself, which remains in suspension in the air in the form of metal microparticles or metal derivatives.
These microparticles are rich in nickel and hexavalent chromium, with a size of 0.01 – 0.1 µm. Once inhaled, these microparticles can penetrate inside the lungs and, with time, in the blood.
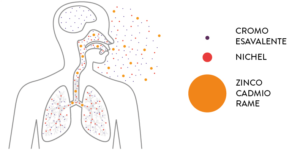
These substances are responsible for diseases of the nervous and respiratory systems, and in the event of prolonged exposure may cause irreversibly damage to operator’s health.
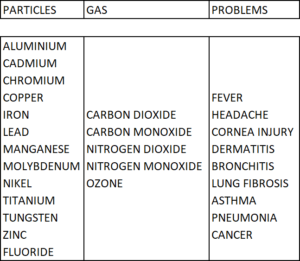
Coughing, chronic sputum, bronchitis and asthma are the mildest effects. As the inhalation of welding fumes continues over time, and iron oxides accumulate in the pulmonary alveoli, serious respiratory inflammations may develop, which may lead to serious pneumonia. These accumulations can only be detected by means of a chest X-ray.
The fine particles during welding and laser marking processes are produced during combustion and oxidize on contact with oxygen, releasing harmful gaseous substances. With some of these substances, the risk of fire and explosion must also be taken into consideration.
Coughing, chronic sputum, bronchitis and asthma are the mildest effects. As the inhalation of welding fumes continues over time, and iron oxides accumulate in the pulmonary alveoli, serious respiratory inflammations may develop, which may lead to serious pneumonia. These accumulations can only be detected by means of a chest X-ray.
The fine particles during welding and laser marking processes are produced during combustion and oxidize on contact with oxygen, releasing harmful gaseous substances. With some of these substances, the risk of fire and explosion must also be taken into consideration.
With update 118 of 2018, the IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer) has included welding fumes among the carcinogenic elements for humans, both for the presence of nickel and chromium, and for the exposure to ultraviolet radiation emitted during the process.
The result of reclassification is that any exposure to welding fumes must be properly controlled, with the correct devices.
The most effective method of control is to capture fumes and gases directly at the source before they enter the worker’s respiratory tract or are dispersed throughout the working area.
The result of reclassification is that any exposure to welding fumes must be properly controlled, with the correct devices.
The most effective method of control is to capture fumes and gases directly at the source before they enter the worker’s respiratory tract or are dispersed throughout the working area.
In order to properly purify the air from these microparticles, our fume extractors are equipped with a progressive filtration system consisting of panel filters capable of trapping even the smallest particles.
The 4 stages of filtration are composed as follows:
The 4 stages of filtration are composed as follows:
- a metallic filter with an anti-spark trap
- a fireproof pre-filter to prevent possible ignitions
- a main filter F8 with a large filtering surface 16sqm
- a last stage variable depending on the use, with the possibility of 12kg of active carbon or absolute filter H13 with 34sqm of filtering surface area.
Protect yourself and your operators with Du-Puy fume cleaners, it’s time to think about your health and your future!